The world is facing an unprecedented environmental crisis, and businesses are increasingly being held accountable for their impact on the planet and society. As a result, the financial industry is recognizing the importance of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations in investment decision-making. However, with no universal framework for reporting ESG data, financial institutions face significant challenges in assessing the sustainability performance of companies.
Standardization of ESG data is critical to enable financial institutions to effectively evaluate and compare the sustainability performance of companies, develop ESG-focused investment products, and promote transparency and accountability in ESG reporting. Here, we explore the significance of ESG data standardization in the Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) sector, the challenges faced, and how standardization helps drive a more sustainable future.
According to Statista, the value of assets allocated to ETF funds that incorporate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into their investment strategies has risen significantly.
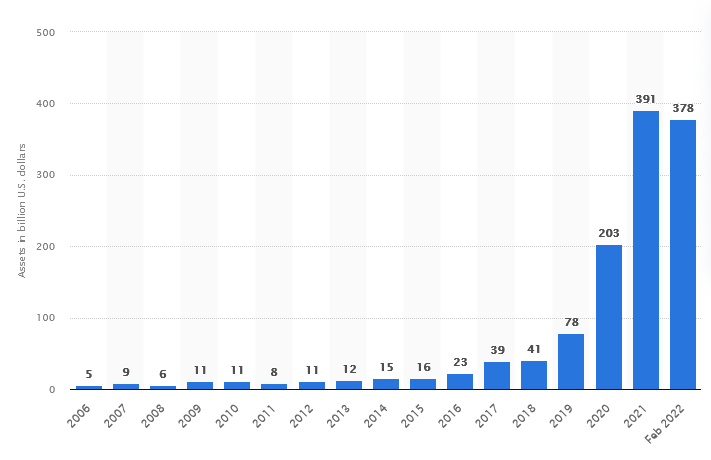
Global ESG ETF assets 2006-2022
From only five billion U.S. dollars in 2006, it has surged to 391 billion U.S. dollars by 2021, and as of February 2022, it reached 378 billion U.S. dollars. This rise in investment in sustainable funds, particularly ETFs, has been mainly driven by developed markets, particularly in Europe and the United States.
The Benefits of ESG Data Standardization in BFSI
ESG data standardization in the Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) sector has a range of benefits for investors, companies, and other stakeholders. Here are some of the key benefits:
- For Investors:
- Improved decision-making: ESG data standardization helps investors to make more informed investment decisions, as they compare the sustainability performance of different companies using a consistent framework.
- Reduced risk: Standardization helps investors to identify companies with strong ESG performance, which may indicate a lower risk of future legal or reputational issues.
- Increased transparency and accountability: Standardization promotes transparency and accountability in ESG reporting, ensuring that investors have access to accurate and relevant information.
- For Companies:
- Improved ESG reporting: Standardization leads to improved ESG reporting practices, as companies are required to report their sustainability performance using a consistent framework. This helps to ensure that the data provided is accurate, relevant, and comparable across companies and industries.
- Enhanced reputation: Companies with strong ESG performance may attract more investment and customers, which enhances their reputation and increases their market value.
- Opportunities for innovation: Standardization creates opportunities for innovation, as companies may develop new products and services that meet the needs of sustainable investors.
- For Other Stakeholders:
- Improved social and environmental outcomes: Standardization promotes sustainability and drives positive social and environmental outcomes by encouraging companies to improve their ESG performance.
- Greater stakeholder engagement: Standardization facilitates greater engagement with stakeholders, such as customers, employees, and communities, as companies may be required to disclose more information about their sustainability performance.
ESG data standardization leads to improved decision-making, reduced risk, increased transparency and accountability, and opportunities for innovation, making it a critical component of sustainable investing in the BFSI sector.
Challenges of ESG Data Standardization in BFSI
ESG criteria are increasingly becoming critical components for evaluating the sustainability and societal impact of businesses. The BFSI, in particular, is under pressure to improve its ESG practices, as investors and customers demand greater transparency and accountability. To meet these demands, the BFSI industry needs to standardize its ESG data collection and reporting processes. However, this process presents both technical challenges and opportunities.
- Data Quality and Consistency: ESG data is often collected from different sources, such as company reports, third-party providers, and industry benchmarks. This data is often unstructured and incomplete, making it difficult to ensure its accuracy and consistency. For example, some companies may report their ESG metrics differently, making it challenging to compare them with other companies. Additionally, ESG data may not be audited, making it challenging to verify its accuracy.
- To address this challenge, BFSI companies implement data quality checks and validation processes. They use technologies such as data governance tools, data cleansing tools, and data profiling tools to ensure that the data is consistent and accurate.
- JPMorgan Chase & Co. uses a data governance platform to validate the accuracy of ESG data reported by its clients. The platform compares the client’s data to industry benchmarks and identifies discrepancies that need to be addressed.
- Data Integration: ESG data is often collected from multiple sources, and the data format may vary. The data integration process involves normalizing the data, ensuring consistency, and reducing errors. The integration process could be complicated, time-consuming, and expensive, making it a significant challenge for BFSI companies.
- To tackle this challenge, BFSI companies use technologies such as data integration tools, application programming interfaces (APIs), and data warehouses to integrate the data. They also implement data governance policies and procedures to ensure that the data is standardized and consistent.
- BlackRock, the world's largest asset manager, uses a data warehouse to integrate ESG data from various sources, such as company reports and third-party providers. The data warehouse enables BlackRock to access standardized ESG data and perform analysis to inform its investment decisions.
- Regulatory Compliance: BFSI companies are subject to regulatory requirements that mandate the disclosure of ESG-related information. However, the regulatory requirements may differ across countries and regions, making it challenging to comply with all of them. Additionally, the regulatory requirements may change over time, making it challenging for BFSI companies to keep up with the changes.
- To overcome this challenge, BFSI companies implement regulatory compliance programs that monitor regulatory requirements and changes. They also use regulatory technology (RegTech) solutions that automate the compliance process and provide real-time alerts for changes in regulations.
- State Street Corporation, a leading financial services company, uses a RegTech platform to monitor regulatory requirements and changes related to ESG reporting. The platform provides real-time alerts and enables State Street to comply with regulatory requirements efficiently.
Opportunities of ESG Data Standardization in BFSI
- Improved Decision-making: Standardizing ESG data across the BFSI industry improves decision-making by providing accurate and reliable data to investors, customers, and regulators. This data is used to assess the risks and opportunities associated with a company's ESG practices, providing valuable insights for investors and businesses. Standardized ESG data also help BFSI companies identify ESG-related risks and opportunities that may impact their long-term sustainability.
- MSCI, a provider of investment decision support tools, offers ESG ratings that enable investors to compare companies’ ESG performance. The ratings provide standardized ESG data that investors use to assess the risks and opportunities associated with a company’s ESG practices.
- Innovation: Standardizing ESG data creates opportunities for innovation in the BFSI industry. It helps develop new financial products and services that are tailored to meet the ESG demands of customers and investors. For example, BFSI companies develop ESG investment products that align with customer values and preferences. Standardized ESG data also helps BFSI companies develop ESG risk management solutions that mitigate ESG-related risks.
- UBS, a Swiss multinational investment bank, has developed an ESG ETF that tracks the MSCI ACWI ESG Leaders Index, which includes companies with high ESG ratings. The ETF enables investors to invest in companies that prioritize ESG practices and align with their values.
- Brand Reputation: Companies that prioritize ESG practices and reporting enhance their brand reputation and attract more investors and customers. Standardized ESG reporting provides transparency and accountability, which is crucial in building and maintaining trust with stakeholders. Companies that prioritize ESG practices may also be better positioned to attract and retain top talent, as employees increasingly prioritize companies according to their convenience.
- Unilever, a consumer goods company, publishes an annual Sustainable Living Report that outlines its ESG performance and goals. The report provides transparency and accountability, which enhances Unilever’s reputation and helps it build trust with stakeholders. Additionally, Unilever’s ESG practices have helped it attract and retain top talent, as employees increasingly prioritize companies that align with their values.
Conclusion
The future of ESG data standardization in the BFSI industry looks bright, with continued growth in demand, technological advancements, and regulatory initiatives all driving the industry forward. Standardization and transparency in ESG reporting will become increasingly important, and investors will continue to rely on ESG data to make informed investment decisions.
The future of ESG data standardization will likely be characterized by greater collaboration between investors, companies, and regulators, as stakeholders work together to promote sustainability and transparency in the financial markets.

















