A Closer Look at GenAI’s Adoption Across Key Sectors
“Generative AI emerges as a critical technological catalyst, driving unprecedented transformation across healthcare, finance, retail, education, and logistics. Strategic implementation of GenAI promises substantial operational efficiency, innovative solutions, and competitive advantage for forward-thinking organisations.”
Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) represents a transformative technological paradigm that is fundamentally reshaping organisational strategies across global industries. This sophisticated technological innovation transcends traditional computational boundaries, offering unprecedented capabilities in content generation, predictive analytics, and intelligent problem-solving. The strategic significance of GenAI lies not merely in its technological sophistication but in its potential to redefine operational frameworks, decision-making processes, and competitive positioning for enterprises worldwide.
The contemporary business landscape demands continuous technological adaptation, and GenAI emerges as a critical enabler of this evolutionary process. By providing intelligent, context-aware solutions that can generate, interpret, and analyse complex datasets, GenAI is establishing itself as a pivotal technological infrastructure for organisations seeking sustainable competitive advantage. This comprehensive analysis will explore the multifaceted implications of GenAI across diverse industrial ecosystems, elucidating its strategic potential and implementation methodologies.
The Evolution of AI and the Emergence of GenAI
The trajectory of artificial intelligence represents a remarkable journey of technological progression, transitioning from rule-based systems to sophisticated machine learning algorithms and now to generative models. Traditional AI frameworks were predominantly focused on pattern recognition and predictive analytics, with limited generative capabilities. Machine learning introduced adaptive algorithms capable of improving performance through experience, while deep learning enabled neural networks to process complex, unstructured data with remarkable accuracy.
Generative AI distinguishes itself through its capacity to create novel content, solutions, and predictions by learning from extensive training datasets. Unlike predecessor technologies that primarily analysed and classified information, GenAI can synthesise original outputs across multiple domains, including text, imagery, code, and complex strategic scenarios. This fundamental shift represents a technological quantum leap, enabling machines to not just interpret but actively generate intelligent, contextually relevant content.
The breakthrough nature of GenAI lies in its advanced neural network architectures, particularly transformer models and large language models that can comprehend and generate human-like responses. These models leverage sophisticated probabilistic algorithms and massive computational resources to understand intricate contextual nuances, enabling unprecedented levels of intelligent content generation and complex problem-solving capabilities.
The Business Case for GenAI Adoption
Quantifying the economic value of GenAI reveals compelling arguments for strategic investment. Conservative estimates suggest potential productivity gains ranging between 10-20% across multiple organisational functions. [1], translating into substantial operational efficiencies and cost optimisations. The economic rationale extends beyond immediate financial metrics, encompassing strategic advantages in innovation, customer experience, and competitive differentiation.
Key investment drivers for GenAI include increasingly sophisticated customer expectations, accelerating digital transformation imperatives, and the necessity for intelligent automation. [2] Organisations recognising GenAI’s strategic potential are positioning themselves to develop adaptive, intelligent operational frameworks that can rapidly respond to complex market dynamics. This approach transcends traditional technological adoption, representing a holistic reimagination of organisational capabilities.
Strategic considerations demand a nuanced approach to GenAI implementation. Successful integration requires comprehensive risk management strategies, robust governance frameworks, and a culture of continuous learning. [3] Enterprises must balance technological innovation with ethical considerations, ensuring responsible AI deployment that prioritises transparency, accountability, and human-centric design principles.
The Imperative for Reinvention in Modern Organisations
Contemporary organisations face unprecedented challenges in maintaining relevance within rapidly evolving technological landscapes. Customer expectations have transformed dramatically, demanding personalised, instantaneous, and intelligent interactions across multiple touchpoints. Traditional operational models are increasingly insufficient for addressing these complex requirements, creating a critical need for strategic technological reinvention.
Generative AI emerges as a strategic mechanism for digital transformation, offering organisations sophisticated tools to reimagine their operational architectures. By integrating intelligent systems that can dynamically adapt, learn, and generate contextually relevant solutions, enterprises can develop more agile, responsive, and intelligent organisational frameworks. This technological integration transcends mere automation, representing a fundamental restructuring of strategic capabilities.
Leadership plays a pivotal role in driving AI-powered change. Successful GenAI implementation requires visionary executives who can navigate complex technological landscapes, balance innovation with risk management, and cultivate a culture of continuous learning and technological adaptation. Strategic leaders must develop comprehensive AI roadmaps that align technological investments with broader organisational objectives, ensuring sustainable and meaningful digital transformation.
GenAI's Transformative Potential Across Industries
Generative AI’s transformative potential manifests distinctively across various industrial ecosystems, offering nuanced solutions tailored to specific sectoral challenges. Each industry presents unique opportunities for GenAI integration, ranging from operational efficiency improvements to groundbreaking innovation in product and service delivery.
The technological versatility of GenAI enables organisations to address complex challenges through intelligent, adaptive solutions. By leveraging advanced machine learning algorithms and sophisticated neural networks, enterprises can develop highly contextualised strategies that respond dynamically to evolving market conditions. This approach represents a significant departure from traditional, static operational models.
Case studies across multiple sectors demonstrate GenAI’s profound impact. For instance, in healthcare, GenAI has been instrumental in developing personalised treatment protocols. A notable example is the collaboration between IBM Watson Health and Mayo Clinic, where GenAI was used to match patients with appropriate clinical trials, significantly improving patient outcomes.[4] In financial services, GenAI has enhanced risk management strategies. JPMorgan Chase, for example, employs GenAI to analyse vast datasets for fraud detection, reducing false positives by 20%.[5]
In the retail sector, GenAI is revolutionising customer experiences and supply chain management. Companies like Amazon use GenAI to personalise shopping experiences, predicting customer preferences and optimising inventory management.[6] In manufacturing, GenAI aids in predictive maintenance and process optimisation. Siemens, for instance, utilises GenAI to predict equipment failures and streamline production processes, resulting in a 15% increase in operational efficiency.[7]
The education sector also benefits from GenAI, with applications in personalised learning and administrative automation. Platforms like Coursera leverage GenAI to tailor educational content to individual learning styles, enhancing student engagement and outcomes.[8] In logistics, GenAI optimises route planning and demand forecasting. DHL employs GenAI to improve delivery efficiency and reduce operational costs by 10%.[9]
These examples illustrate how GenAI is reconfiguring fundamental operational space. The technology’s ability to process vast datasets, generate predictive insights, and create intelligent, context-aware solutions positions it as a critical strategic asset for forward-thinking organisations.
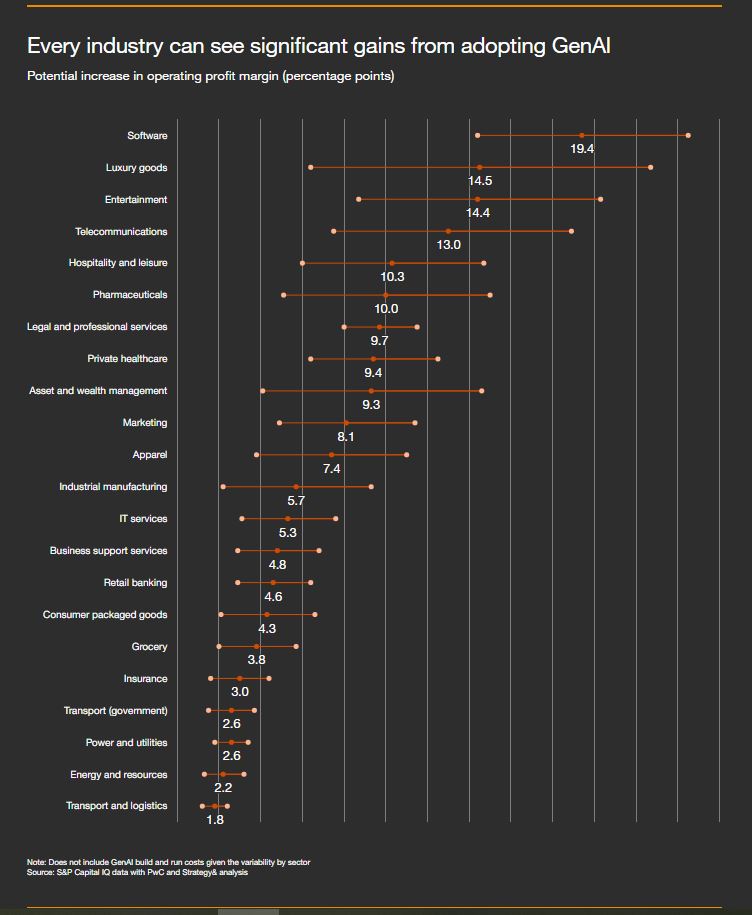
Image Source : PWC
Strategic Implications of GenAI Adoption
The competitive landscape is experiencing fundamental restructuring through GenAI integration. Organisations that successfully implement intelligent technologies are creating significant differentiation, developing capabilities that extend far beyond traditional competitive advantages. This transformation involves comprehensive reconfiguration of workforce skills, technological infrastructure, and strategic thinking.
Talent requirements are evolving rapidly, demanding professionals with hybrid skill sets combining technological proficiency, strategic thinking, and adaptability. Enterprises must invest substantially in upskilling programmes, creating learning ecosystems that enable continuous technological adaptation. The future workforce will require sophisticated capabilities in managing, interpreting, and strategically leveraging intelligent technological systems.
Investment priorities are shifting towards technologies that offer intelligent, scalable solutions. GenAI represents a critical infrastructure investment, enabling organisations to develop more responsive, adaptive operational frameworks. Strategic positioning now depends on an organisation’s capacity to integrate intelligent technologies seamlessly across multiple functional domains.
Key Applications of GenAI
Generative AI’s applications represent a sophisticated technological palette, offering intelligent solutions across multiple organisational functions. Here are six key applications explained in more technical detail:
- Q&A Bots: These bots leverage advanced natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms to provide instantaneous, contextually relevant customer interactions. Unlike traditional scripted responses, GenAI-powered Q&A bots can understand and generate human-like responses, adapting to the nuances of user queries. They utilise transformer models, such as GPT-4, to comprehend context and intent, enabling dynamic and personalised communication strategies that enhance customer satisfaction and engagement.
- Summarisation: GenAI-driven summarisation technologies employ deep learning models to process and condense complex information landscapes rapidly. These models, often based on transformer architectures, can analyse extensive documentation and extract key points to generate concise, meaningful summaries. This capability is particularly valuable for organisations dealing with large volumes of data, as it enables quick assimilation of critical information, facilitating informed decision-making and efficient knowledge management.
- Digital Personas: Digital personas are created using advanced machine learning techniques to simulate human-like interactions. These personas are trained on vast datasets to understand and replicate human behaviour, language patterns, and emotional responses. They are used in customer service, training, and communication platforms to provide engaging, interactive experiences. By leveraging neural networks, digital personas can adapt to user interactions, offering personalised and contextually appropriate responses that enhance user engagement and satisfaction.
- Content Personalisation: GenAI enables organisations to generate highly targeted, individualised content by analysing user data and preferences. Using machine learning algorithms, GenAI can predict user interests and tailor content accordingly. This application is crucial for marketing and customer engagement, as it allows for the creation of personalised experiences that resonate with individual users. Techniques such as collaborative filtering and content-based filtering are employed to deliver relevant recommendations and customised content.
- Code Generation: GenAI is transforming software development processes through automated code generation. By converting natural language descriptions into executable code, GenAI reduces the complexity and time required for software development. Models like OpenAI Codex can understand programming languages and generate code snippets, enabling rapid prototyping and iterative development. This application not only accelerates development cycles but also helps in maintaining code quality and consistency.
- Semantic Searches: Semantic search capabilities leverage GenAI to provide advanced knowledge discovery mechanisms. Unlike traditional keyword-based searches, semantic searches understand the context and intent behind queries, delivering more accurate and relevant results. These searches use deep learning models to analyse the relationships between words and concepts, enabling the extraction of nuanced insights from extensive datasets. This application is particularly beneficial for research and data-intensive industries, as it enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of information retrieval.
Sector-Specific Insights
Healthcare represents a critical domain for GenAI implementation, offering transformative potential in diagnostics, patient care, and administrative efficiency. According to a Gartner survey, 84% of healthcare provider executives believe large language models (LLMs) will have a significant (35%), transformative (37%), or disruptive (12%) impact on the healthcare industry.[10]
Financial services leverage GenAI for advanced fraud detection, risk management, and customer service strategies. Moody’s reports that users of their GenAI tools have experienced a 27% increase in time savings and access 60% more data, significantly improving decision-making efficiency.[11]
Retail sectors utilise GenAI for personalising shopping experiences and optimising supply chain management. McKinsey estimates that GenAI could add between $240 billion to $390 billion in economic value for retailers, equivalent to a margin increase of 1.2 to 1.9 percentage points.[12]
Manufacturing benefits from GenAI through predictive maintenance and process optimisation. According to Cognizant, GenAI can improve quality control, reduce downtime, and enhance overall efficiency, with 27% of manufacturing companies actively investing in GenAI technologies.[13]
Education sees significant advantages with GenAI, particularly in personalised learning and administrative automation. A survey by Cengage found that the use of GenAI among college instructors nearly doubled from 24% in 2023 to 45% in 2024, with 90% believing it will play an increasingly important role in education.[14]
Logistics is another sector where GenAI optimises route planning and demand forecasting. Gartner predicts that by 2028, 25% of all logistics key performance indicator (KPI) reporting will be powered by GenAI.[15]
These data points illustrate how GenAI is reconfiguring fundamental operational paradigms across various sectors. The technology’s ability to process vast datasets, generate predictive insights, and create intelligent, context-aware solutions positions it as a critical strategic asset for forward-thinking organisations.
Cross-Functional Benefits of GenAI
Generative AI delivers substantial efficiency gains across organisational functions, creating intelligent interconnected systems that enhance productivity and strategic decision-making. Marketing departments can develop highly targeted campaigns by analysing customer data to predict preferences and behaviours, resulting in more effective and personalised marketing strategies. Human resources can streamline recruitment processes through automated resume screening and candidate matching, significantly reducing time-to-hire and improving the quality of hires. Data analytics teams can generate sophisticated predictive models that provide actionable insights, enabling better forecasting and strategic planning.
Productivity enhancements emerge through intelligent automation of complex, repetitive tasks. GenAI enables organisations to redirect human cognitive resources towards more strategic, creative endeavours. For example, automated report generation and data entry allow employees to focus on higher-value tasks such as strategic analysis and innovation. Customer satisfaction improves through personalised, intelligent interactions that demonstrate a deep understanding of individual preferences and requirements. GenAI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide instant, accurate responses to customer inquiries, enhancing the overall customer experience.
Competitive advantages are generated through the capacity to develop more responsive, intelligent organisational architectures. Enterprises can create dynamic strategies that adapt rapidly to changing market conditions, leveraging intelligent technologies as strategic assets. By integrating GenAI across various functions, organisations can achieve a holistic transformation that enhances agility, innovation, and resilience. This strategic integration positions companies to respond proactively to market shifts, maintain a competitive edge, and drive sustainable growth.
Strategic Risk Management in GenAI Adoption
Comprehensive risk assessment frameworks become critical in managing GenAI implementation. Organisations must develop robust governance strategies that balance technological innovation with ethical considerations, data privacy protection, and regulatory compliance. This requires a sophisticated, multi-dimensional approach to technological integration, ensuring that all potential risks are identified and mitigated effectively.
Talent acquisition strategies must evolve to attract professionals capable of managing complex intelligent systems. Skill development programmes should focus on creating hybrid capabilities that combine technological proficiency with strategic thinking. This involves investing in continuous learning and development initiatives to keep the workforce updated with the latest advancements in GenAI. Ethical AI principles must be embedded deeply within organisational cultures, promoting transparency, accountability, and fairness in all AI-driven processes.
Performance measurement becomes increasingly sophisticated, requiring advanced metrics that capture the nuanced value generation of intelligent technologies. Return on investment calculations must consider both quantitative efficiency gains and qualitative strategic advantages. This includes evaluating the impact of GenAI on innovation, customer satisfaction, and competitive positioning. By adopting a holistic approach to performance measurement, organisations can ensure that their GenAI initiatives deliver sustainable value and align with broader strategic objectives.
The Future of GenAI in Industry
Expected technological advancements in GenAI suggest increasingly sophisticated, context-aware intelligent systems. These systems will be capable of understanding and responding to complex contextual nuances, enabling more accurate and relevant outputs. Emerging business models will likely prioritise adaptive, intelligent infrastructures that can generate dynamic strategies in real-time, responding swiftly to market changes and customer needs.
The boundaries between human and machine intelligence will continue to blur, creating more integrated, collaborative technological ecosystems. This integration will enhance the synergy between human creativity and machine efficiency, leading to innovative solutions and improved decision-making processes. AI-native enterprises will emerge, developing organisational architectures fundamentally designed around intelligent technological capabilities. These organisations will demonstrate unprecedented agility, developing strategies that can adapt instantaneously to complex, dynamic market conditions.
The competitive landscape will be increasingly defined by an organisation’s capacity to integrate, manage, and strategically leverage intelligent technologies across multiple functional domains. Companies that excel in harnessing GenAI will gain a significant competitive edge, driving innovation, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. As GenAI continues to evolve, its role in shaping the future of industry will become even more pronounced, making it a critical component of strategic planning and execution.
Conclusion
Generative AI represents a critical technological infrastructure for contemporary organisations, offering unprecedented capabilities in intelligent content generation, strategic analysis, and adaptive problem-solving. The strategic potential extends far beyond technological innovation, representing a fundamental reimagination of organisational capabilities.
Enterprises must adopt proactive, strategic approaches to AI integration, developing comprehensive roadmaps that balance technological innovation with ethical considerations. This involves not only leveraging the technological advantages of GenAI but also ensuring that its implementation aligns with ethical standards and regulatory requirements. The future belongs to organisations capable of developing intelligent, adaptive technological ecosystems that can respond dynamically to evolving market conditions and customer needs.
By adopting GenAI, organisations can position themselves at the forefront of innovation, driving sustainable growth and maintaining a competitive edge in an increasingly complex and dynamic business environment.
About the author : Dr. Bishan Chauhan, Head – Cloud Services & AI / ML Practice, Motherson Technology Services























