Over the years, the rise of cloud computing, remote work, and IoT devices has expanded the attack surface of enterprises, leading to increased digital risks and cyber threats. Traditional perimeter-based security models, where trust was automatically granted to users within the network, have become ineffective in this decentralized environment. Zero Trust security eliminates the blind spots left by these outdated models by assuming that every access request could potentially be a security risk.
This blog explores why Zero Trust is the future of cybersecurity for organizations and what separates Zero Trust from traditional security. Discover what Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) really is and how it protects against cyber threats by optimizing network security architectures.
Zero Trust Security Framework Explained
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is a modernized security framework designed to protect businesses from cyber threats by assuming that no one—whether inside or outside the organization's network—can be trusted by default. Instead of trusting devices or users just because they are within the network security architecture, Zero Trust continuously verifies and authenticates every user, device, and application before granting access to any data or resource. The goal is to minimize the chances of a breach by giving the least privilege necessary and constantly monitoring all activities.
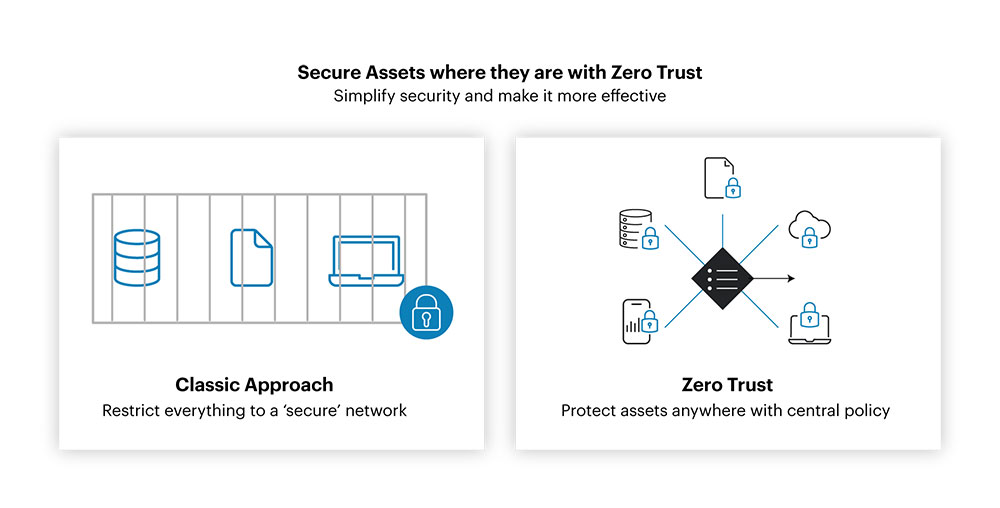
Simply put, Zero Trust Architecture works like having a bouncer at every door, ensuring only the right people get in and that they're continuously checked while inside.
Importance of Zero Trust Security
Cyberattacks are now far more advanced and targeted, putting even the most secure enterprises at risk. Tech giants like Microsoft, Google, and Amazon have long been at the forefront of Zero Trust security to address evolving cyber threats. With vast amounts of proprietary data and intellectual property to protect, their increased focus on implementing Zero Trust aims to prevent unauthorized access and ensure continuous security within their development and operational environments.
In a world where breaches are inevitable, there are three main reasons Zero Trust policy enforcement is critical to minimize threats and ensure business continuity.
• Evolving Threat Landscape: Cyberattacks like ransomware, phishing, and supply chain breaches are becoming more targeted and advanced, bypassing traditional security. By verifying each access request and minimizing unnecessary access, Zero Trust reduces the potential damage from these threats, ensuring only essential user activity.
• Data Decentralization: With more employees working remotely, sensitive data is spread across various locations, increasing the attack surface. Zero Trust secures every access point, ensuring data is protected no matter where it's accessed from, using encryption and continuous authentication.
• Cloud and IoT Expansion: The growth of cloud and IoT devices introduces more potential vulnerabilities. Zero Trust security treats each device and application as untrusted, continuously monitoring and securing them to protect data and infrastructure.
As remote work decentralizes data and cloud/IoT devices create new vulnerabilities, businesses are constantly pushing for more inventive and robust security protocols. Rapid7's Ransomware Report 2024 identified that there had been a 67% upsurge in ransomware groups posting to leak sites in the first half of 2024. Ransomware and phishing are becoming more advanced, even targeting highly secure organizations. Zero Trust architecture becomes crucial for minimizing such threats by attentively verifying every access point and securing critical infrastructure.
What Companies Should Know About Adopting Zero Trust Security
As cloud adoption soars, understanding how Zero Trust Architecture will secure cloud environments is pivotal for business continuity.
In a global survey by Vanson Bourne and VMWare, 95% of companies state that multi-cloud architecture is integral to business success. As numerous cloud platforms and technologies come together to organize business capabilities, implementing top-notch security strategies is indispensable. With decentralized data workloads, third-party software, and numerous stakeholders involved, securing every access point is a no-brainer. To handle multi-cloud complexities, Zero Trust Architecture proves to be the most reliable among IT security strategies. Here's why!
Security frameworks have evolved from a perimeter-based model, which relied on securing the network's outer boundary, to Zero Trust Architecture, which assumes that threats can come from both inside and outside the network. Zero Trust establishes a security model through a proactive approach for businesses to tackle complexities in governance and maintain reinforced security.
The main difference is that perimeter-based security trusts everything within the network once authenticated, while Zero Trust verifies every access request, regardless of where it originates, ensuring continuous security throughout the system. By reducing the surface of exposure to risks, Zero Trust framework's security strategies prioritize real-time monitoring and rapid response.
Zero Trust Architecture: Key Components and Best Practices
No two industries face the same challenges when it comes to cybersecurity, which is why Intelliswift strategizes network security architectures based on business operations to deploy modernized security frameworks. Whether it is a healthcare provider protecting patient data, a financial institution securing transactions, or a tech company safeguarding intellectual property, businesses can mitigate losses by employing Zero Trust network access (ZTNA) solutions.
Here are key steps to implement a Zero Trust security model in your business:
1. Verify Everything: Always assume that no one is trustworthy by default. It is like checking everyone's ID whenever they try to enter, even if they've been inside before. Every user, device, and action must be verified before being allowed access.
2. Least Privilege Access: Only give people the bare minimum access they need to perform their job. Just because someone works in the building does not mean they should have keys to every room. They only get access to the places necessary for their role.
3. Micro-Segmentation: Break down the network into smaller zones to ensure that if one part is breached, the whole system isn't compromised. It's like having several doors in a building, each locked separately, so getting through one doesn't mean full access to everything.
4. Continuous Monitoring: This is like having security cameras watching every room, not just the entrance, to spot anything unusual in real time. Keep an eye on all activities happening across the network, looking for suspicious behavior or unauthorized access.
5. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Use more than one method of verification, like a password plus a fingerprint or a security token, to ensure the person accessing is who they claim to be, requiring not just an ID but also a second form of verification, like a badge, to prove someone's identity.
6. Encryption: Imagine that every message sent is locked in a coded box, and only those with the right key can unlock and read it. Encrypt all data, whether it is being stored or transferred, so that even if intercepted, it can't be easily read or used.
Zero Trust Architecture for Enterprises
Industry leaders recognize the importance of Zero Trust in combating today's cyber challenges, with many advocating for its adoption across sectors. In this environment, Intelliswift leads the way by offering tailored ZTNA solutions that combine AI-driven threat detection, real-time security monitoring, and strict access control protocols to ensure business continuity and security from even the most advanced cyber threats. By integrating AI-driven threat intelligence, organizations stay ahead of potential attacks, ensuring effective security and preparedness to tackle ever-evolving digital risks.
To highlight why Zero Trust matters for businesses, here are some examples of Zero Trust implementation across leading US corporations.
• Amazon has implemented Zero Trust within its AWS infrastructure to protect customer data and ensure secure transactions on its global platform. By using micro-segmentation and enforcing strict access controls, Amazon prevents data breaches while maintaining fast and reliable service for its customers.
• The US Department of Defense (DoD) has implemented a Zero Trust framework to protect its networks from cyber espionage and sabotage. By enforcing strict identity and device verification, the DoD ensures that only authorized personnel have access to critical data, even when working remotely.
• Microsoft has taken a Zero Trust approach to protect its sprawling cloud infrastructure, Azure. By leveraging strong authentication, access policies, and end-to-end encryption, Microsoft has enhanced its ability to defend against nation-state attacks and ensure the security of customer data on its platforms.
Benefits of Zero Trust Security
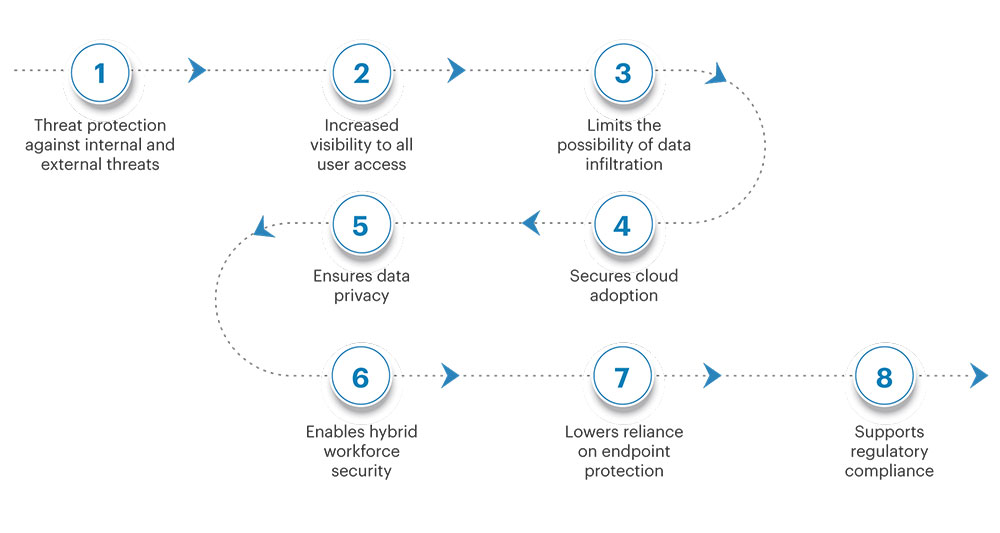
As data systems process more complex workloads, businesses face bigger security challenges, where Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) offers a comprehensive and flexible way to protect against cyber threats. With Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), companies can guard against both internal and external risks, while improving control over who accesses data. This approach reduces the chances of data breaches by constantly monitoring network activity. By keeping data private and supporting the secure use of cloud technology, Zero Trust also strengthens hybrid work setups. It goes beyond traditional security methods to help businesses stay secure, meet regulations, and remain adaptable in a fast-changing, data-driven world.


















