Congratulations! You are now the proud owner of a domain name -your online identity! By registering your domain name, you have taken one more step towards establishing your brand online.
Now you must be having a lot up your sleeves- discussions about creating that perfect website, best web hosting plan that best suits your needs and a lot more.
Among all these chores, managing the domain that you have just taken may seem like a formidable task. But don’t worry, this step by step guide will make different tasks that you have to perform for your domain management a cakewalk.
By logging into your member panel, you can easily access different aspects of your domain management at a single place by following the path provided below:
My Services >Current Domains> Domain Control Center
When you click on a domain name, you will see multiple tabs which are explained in detail here.
What are WHOIS Details and how do I change them?
In order to keep up with ICANN regulations, you need to provide your authentic details like your name, your organization’s name, address, email address, where and when was the domain registered, name servers associated with the domain, etc. All this information provided by you is accessible via a public domain WHOIS search.
- Registrant Contact: This information appears at top of WHOIS lookup. These are the details about the owner or registrant of the domain- it can be a company or an individual entity.
- Administrative contact: Always keep the email address in these details up-to-date as these are the contact details of that person who is allowed to make changes to the domain.
- Billing Contact: This information is not shown in the WHOIS search. The details of the individual provided here will be responsible for handling billing issues with regard to this domain name registration and all renewal information will also be sent to this address.
- Technical Contact: This information is regarding the individual who handles all issues related to web hosting, mail, DNS, etc. Sometimes this is your web hosting provider’s contact information.
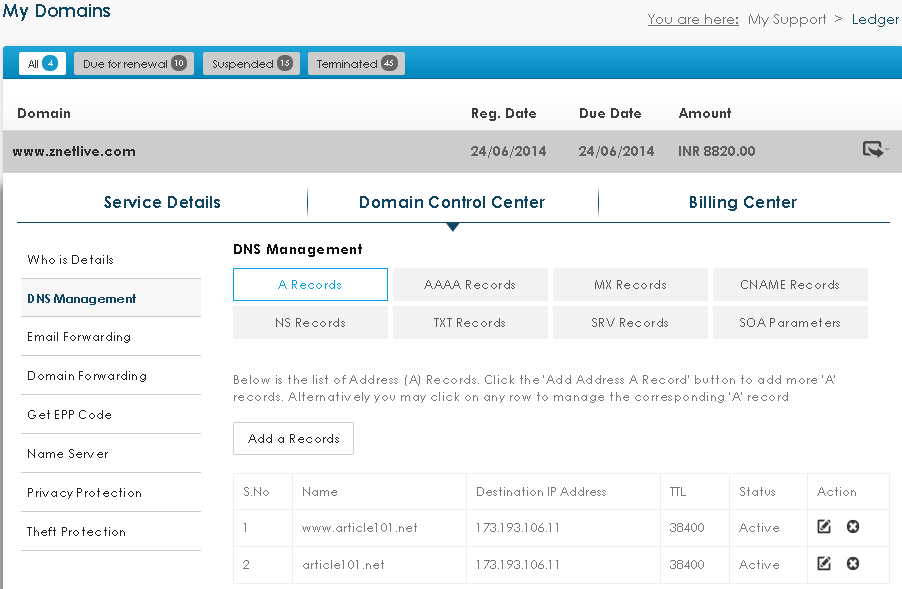
What is DNS Management?
Domain Name System (DNS) is many times called “the phone book of the internet” as it helps in directing internet traffic by converting hostname (like www.znetlive.com) to IP address (like https://69.162.97.219) of that web server which hosts that particular site.
DNS stores the information about names and addresses of almost all public hosts on the World Wide Web in a distributed database.
This is a very pragmatic approach as remembering multiple IP addresses for a number of websites is quite an impossible task.
There are different types of DNS records that give a bird’s eye view about database records stored in DNS zone files. They are explained below:
A Records: Address or A records (also host records) are the central records of DNS. These records link a domain to an IP address. For instance, yourdomain.com has an A record that points to 68.178.232.100.
This means that all traffic to yourdomain.com will be directed to the server with IP address 68.178.232.100. The value of an A record is always an IP address, and multiple A records can be configured for one domain name.
AAAA Records: Similar to A record, an AAAA record points a domain or subdomain to an IPv6 address; but A records only utilize IPv4 addresses.
MX Records: MX records or Mail Exchange records are those basic records that are used for directing email for a domain name. MX records work along with the NS and A records for directing the received email for a particular domain name to the correct mail server.
Normally, MX records are set up with few preferences that indicate the mail servers that should be utilized in the case where several are listed.
CNAME Records: CNAME records or Canonical Name records function as aliases for domain names of other canonical domain name.
This is generally suitable to point domains with a subfolder to a subdomain within a single primary domain name.
For example, the URL https://www.znetlive.com/blog resolves to be exactly similar to the domain https://blog.znetlive.com.
NS Records: NS records or Nameservers are those basic DNS records that enable DNS to translate a domain name to an IP address.
In the absence of these records, IP addresses would need to be remembered for accessing websites rather than through domain names. For instance, the IP address: https://69.162.97.219 resolves to the ZNetLive domain: https://www.znetlive.com/
NS Records are also used for breaking your domain into subdomains. Subdomains indicate you are delegating a portion of a domain name to a different group of name servers, thus generating NS records to point the name of the subdomain to different name servers.
TXT Records: TXT records or Text records are custom records that comprise data readable by human beings. Dynamic TXT records find usage for a number of purposes like domain ownership verification for different services like Google Apps.
SRV Records: SRV records or Service records are utilized for pointing one domain to another domain name by utilizing a particular destination port. SRV records permit specific services, like IM or VOIP, to be guided to a different location.
SOA Parameters: SOA or Start of Authority is the resource record that specifies primary properties of the DNS zone and domain, like e-mail ID of the associated person, the retry and refresh intervals, cache keeping period etc.
What is Email Forwarding?
Email forwarding enables one to direct all incoming traffic on one email ID to another email ID. Whenever any mail is received, our mail servers redirect it to the forwarded mail ID. Messages are only forwarded and not stored on the mail server.
What is Domain Forwarding?
Domain forwarding enables one to direct all incoming traffic on a domain or a parked domain to any working and active website. So when anyone attempts to access your domain name, they are redirected automatically towards the main site.
- URL Masking / Stealth Redirection / URL Hiding- Forwarding alongwith masking ensures that domain is forwarded to the destination website with URL in the address bar remaining the same. Thus, your visitors are able to see the source URL and not the destination URL.
- Sub Domain Forwarding- Subdomain forwarding allows you to redirect any of your subdomains to another domain. For example, subdomain forwarding can be used for forwarding http://subdomain.mydomain.com to http://yourdestinationurl/subdomain/
- Path forwarding- On enabling path forwarding, a visitor to http://yourdomain.com/some/path will get forwarded to http://yourdestinationurl/some/path.
What is EPP Code and how do I get it?
EPP code is an authorization key that is needed by your new registrar for completing the domain transfer from your existing registrar. You can get your EPP code directly from your member panel by visiting the ‘Get EPP Code’ tab.
What is a Name Server and how do I manage NS records?
NS records or Nameservers are those basic DNS records that enable DNS to translate a domain name to an IP address.
In the absence of these records, IP addresses would need to be utilized for accessing websites rather than through domain names. For instance, the IP address: https://69.162.97.219 resolves to the znetlive domain: https://www.znetlive.com/
What is Privacy Protection?
Everyone has to provide accurate contact information while buying a domain name.
This information has to be made publicly available to everyone via the public WHOIS database as required by ICANN, the international governing body for domain name registrations.
Once your contact information is publicly available, you’re at risk for identity theft, fraud and of being contacted by spammers, harassers and stalkers.
When you enable Privacy Protection on a domain name, we replace all your publicly visible contact details with alternate contact information so that when a WHOIS query is performed on the domain, an alternate mailing address, email address and phone number are displayed.
What is Theft Protection?
By enabling theft protection, you can secure your domain from unauthorized transfers. This should be disabled when you intend to transfer out your domain name.